Android琐碎知识记录
使用最新的API,并支持新的硬件
- 新的API效率更高
- 在运行时监测版本
- 使用接口或者平行Activity实现API兼容
对于使用接口和平行Activity的具体做法,记录如下:
平行Activity(The parallel Activity pattern)
private static boolean shinyNewAPIS =
android.os.Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.HONEYCOMB;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
Intent startActivityIntent = null;
if(!shinyNewAPIS)
startActivityIntent = new Intent(this, legacyActivity.class);
else
startActivityIntent = new Intent(this, hcActivity.class);
startActivity(startActivityIntent);
}
接口(The Interfaces for backwards compatibility)
private static boolean newSensorAPIsSupported =
Build,VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.CUPCAKE;
boolean gyroExists =
getPackageManager().hasSystemFeature( PackageManager.FEATURE_SENSOR_GYROSCOPE );
IOrientationSensorListener myListener;
if ( gyroExists )
myListener = new GyroOrientationSensorListener();
else if ( newSensorAPIsSupported )
myListener = new AccOrientationSensorListener();
else
myListener = new AccOldOrientationSensorListener();
使用IntentFilter捕获网页链接( Capture links using Intent Filters )
- Use Intent to capture links.
- Offer the best way to consume your content
- Deep link directly to quivalent content
<activity android:name=".MyActivity">
<intent-filter>
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<data android:scheme="http"
android:host="mysite.com"
android:pathPrefix="/news/articles/" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
内存管理( Memory Managerment )
Heap Size
对于Android应用来说,App的运行时可用内存最小是16M,但是真实出厂的设备内存往往高于这个值,比如
- G1:16M
- *Droid:24M
- N1: 32M
- Xoom:48M
可以使用ActivityManager.getMemoryClass() 读取内存信息。
Large Heaps
一般的Android应用都有一个固定的内存上限,但是对一些特殊的设备(比如平板)屏幕尺寸非常大,即使仅仅展示一张图片所占用的内存也是很可观的,所以在Honeycomb开始引入了largeHeap可以为App分配更多的内存。
在 Honeycomb 以上的系统上可以在AndroidManifest.xml中添加 “largeHeap” 选项。
<application
android:name="com.example.foobar"
android:largeHeap="true"
...
</application>
- ActivityManager.getLargerMemoryClass()
这样可以申请更多的堆内存,申请更多的内存也会增加内存回收的负担,并且迫使其他的App因内存不足被杀死。
Garbage Collection
在垃圾回收方面,给App分贝更大的内存意味着更长的垃圾回收时间,在Gingerbreak之前,垃圾回收会有如下的弊端
- Stop the world
- Full heap collection
- Pause times often > 100ms
在 Gingerbread 之后(包含)改进了上面的弊端
- Concurrent(mostly)
- Partial collections
- Pause times usually <5ms
Bitmaps
Old way (pre-Honeycomb):
- freed via recycled() or finalizer
- hard to debug
- full, stop-the-world GCs
这种方式必须手动调用 recycled 或者 等待垃圾回收才能回收内存。图片占用的内存是在native模块申请的,java对象指向native的内存。Bitmap对象和图片真实内存不再同一个区域。
New way:
- freed synchronously by GC
- easier to debug
- concurrent & partial GCs
Bitmap和图片实际占用的内存都在托管代码部分。
Interpreting Log Message
有木有注意到Logcat中经常打印的信息,比如下面这样的Log 这条log包含了很多信息
D/dalvikvm( 9050 ): GC_CONCURRENT freed 2049K, 65% free 3571K/9991K, external 4703K/5261K, paused 2ms+2ms
- Reason for GC
- GC_CONCURRENT
- GC_FOR_MALLOC
- GC_EXTERNAL_ALLOC
- GC_HPROF_DUMP_HEAP
- GC_EXPLICIT
- Amount freed “freed 2049K”
- Heap statistics “65% free 3571K/9991K”
- External memory statistics “external 4703K(allocated)/5261K(a sort of soft limit)” bitmap pixel data or nio buffer
- Pause time
Heap Dumps
- Binary dump of all object
- Create with: DDMS , android.os.Debug.dumpHprofData()
- Convert to standard HPROF format: hprof-conv orig.hprof converted.hprof
- Analyze with MAT, jhat,etc
MAT
MAT是一个Java程序的内存分析工具,使用它可以发现很多内存泄露的问题,在Android界还是很牛逼的。首先有些基本概念需要明确。
- Shallow heap 指当前对象占用内存的大小
- Retained heap 指当前对象和所持引用的对象(life owned by current object)的大小加
在MAT里面是使用 Dominator(支配者) Tree ( closest object on every path to node)来描述Retained heap 的,比如
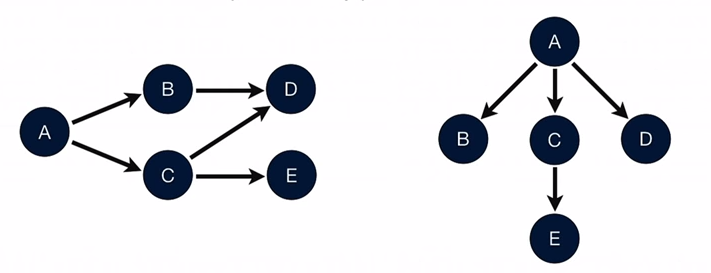
左边是内存中的引用关系,右边是DominatorTree,所有的对象都是依赖A对象而活着的,但是D对象既可以依赖B也可以依赖C活着,所以它不依赖于B,C,而是依赖于A。
使用MAT查泄漏:
- 在DominatorTree视图中,查找RetainedHeap最大的对象,然后找到它的GC-Root (exclude weak reference)。
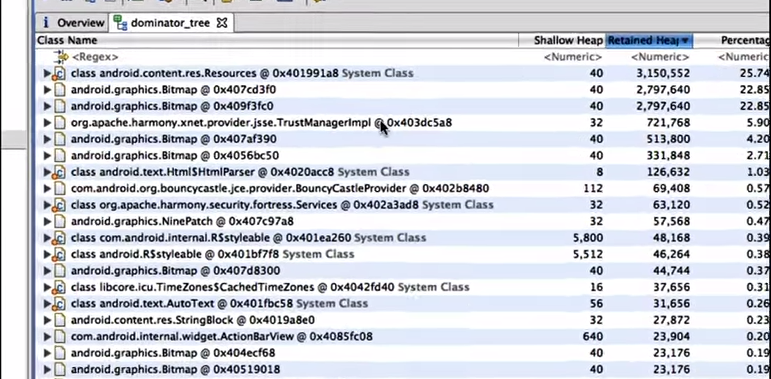
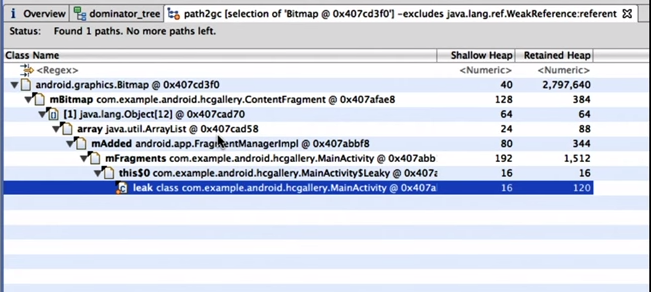
- 在Histogram视图中,查找内存占用最大的对象 => List Objects => GC-Root

- 在Histogram视图中查找对象实例的数量,通过数量判断是否溢出
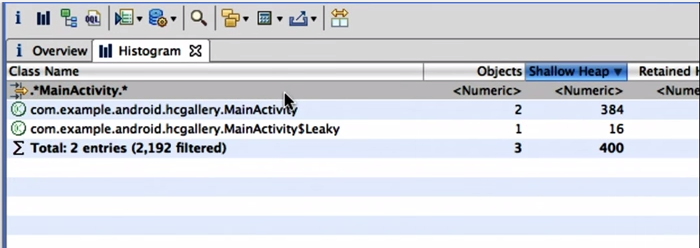
可疑对象
- References to Activity,Context,View,Drawable,…
- Non-static innerr classes(eg: Runnable (延迟执行的Runnable持有一个已经摧毁了的Activity对象)) 小心!
- Caches
Tips:
- Do not keep long-lived references to a context-activity (a reference to an activity should have the same life cycle as the activity itself)
- Try using the context-application instead of a context-activity
- Avoid non-static inner classes in an activity if you don’t control their life cycle, use a static inner class and make a weak reference to the activity inside. The solution to this issue is to use a static inner class with a WeakReference to the outer class, as done in ViewRoot and its W inner class for instance
- A garbage collector is not an insurance against memory leaks
Advanced Android audio techniques
- Native audio signal processing
- Tips on power and resource usage
- What’s new in Froyo?
- Roadmap
AudioTrack Overview
- Raw PCM audio API
- Streaming or static buffers
- Can set callbacks to refill buffer
- Retrieve play position
- Useful for games or streaming audio
Dalvik Virtual Machine Internals
- Intro
- Memory
- CPU
- Advice
- Conclusion
A JIT Compiler for Android’s Dalvik VM
Overview
- View live session notes and ask questions on Google Wave: http:/bit.ly/blzjnF
- Dalvik Environment
- Trace vs. Method Granularity JITs
- Dalvik JIT 1.0
- Future directions for the JIT
- Performance Case Studies
- Profiling JIT’d code
- Built-in Self-Verification Mode