Android Rest-ful Client
这篇文章主要内容来自于对 Video 的笔记,这是一个堪称Android界App设计指南的视频,至今依然具有很好的指导意义。
Rest API Application
首先看一下目前常见的App设计架构

What’s wrong with this approach ?
- The operating system may shut down the process
- Data is not persistently stored
这种设计方式把数据的处理和App中UI/UX控制都混杂在一个Activity(Controller)里面,没有明确的分层,不易维护同时数据没有做缓存,如果App关闭了,那么所有数据下次还要重新加载。
REST Method Implementation Patterns
这里提供了三种实现 REST-ful API 的方式,但是大同小异,重要的是掌握其中的精髓。
-
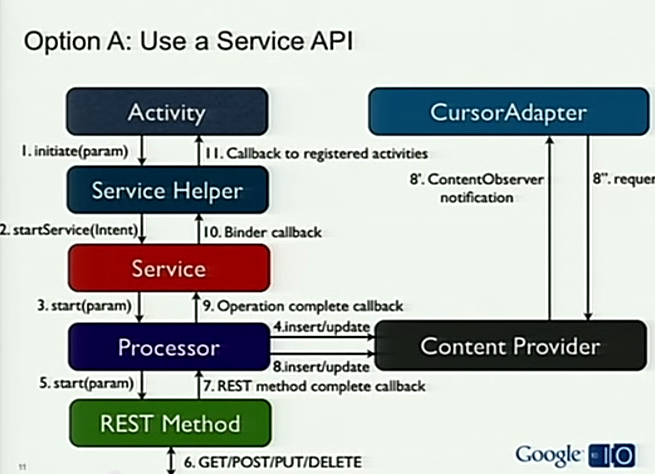
Use a Service API
- Use the ContentProvider API

- Use the ContentProvider and a SyncAdapter
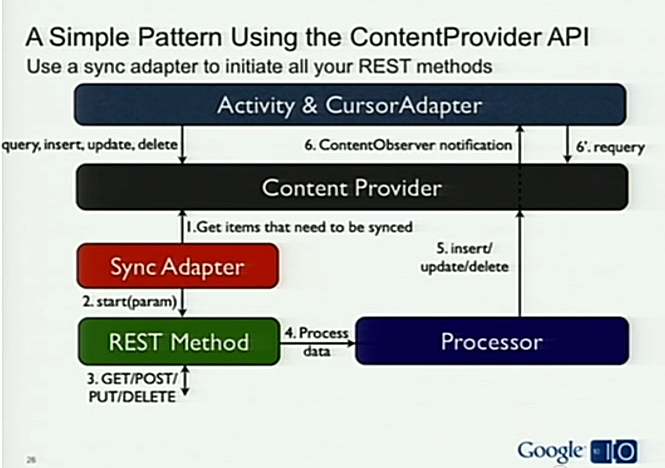
这三张图分别展示App的架构设计,Activity&ServiceHelper属于上层的调用层,Service-Processor-REST_Method 数据处理层,ContentProvider 负责数据存储和对外提供数据。
Use a Service API
REST Method 部分,主要负责网络交互,封装HTTP请求,并把结果处理成一般的格式(现在来看已经有更好的选择来做这一步,比如Google的Volley框架)
- An entity which:
- prepares the HTTP URL & HTTP request body
- Executes the HTTP transaction
- Processes the HTTP response
- Select the optional content type for responses
- Binary,JSON,XML
- New in froyo: JSON parser( same org.json API)
- Enable the gzip content encoding when possible
- Run the REST method in a worker thread
- Use the Apache HTTP client
Tips:
- That’s a great way to mirror the state of the resource in the database and retry these methods
- Never execute database operations or content provider opertation in the Main thread(UI thread)
- Use transactions when you use SQLite(Not only will they preserve the data integrity but hte will increase the performance of your databse opertations)
Service 的存在主要是给 REST Method 提供一个宿主的空间,使之能够独立于Activity,不受Activity生命周期的影响(如果使用Volley框架,其实也没有太大的必要再使用Service)。
- The role of the service is to allow your application to execute opertations in the backgroud while an activity is long gone
- Forward path : receives the Intent sent by the Service Helper and starts the corresponding REST Method
- Return path: handles the Processor callback(failed or worked) and invokes the Service Helper binder callback
- It can implement a queue of downloads (避免多线程下载,应该实现队列)
服务空载时应该及时关闭,避免资源浪费。
Service Helper 封装一些接口给Activity使用,同时处理回调事件
- Singleton which exposes a simple asynchronouses API to be used by the user interface
- Prepare and send the Service request
- Check if the method is already pending
- Create the request Intent
- Add the operation type and a unique request id
- Add the method specific parameters
- Add the binder callback
- Call startService(Intent)
- Return the request id
- Handle the callback from the service
- Dispatch callbacks to the user interface listeners
Handling the REST Method in an Activity
- Add an operation listener in onResume and remove it in onPause
- Consider these cases :
- The Activity is still active when the request completes
- The Activity is paused then resumed and then the request completes
- The Activity is paused when the reuqest completes and then Activity is resumed
(??? 走神了)
使用ContentProvider的一个极大的优点是,可以让UI仅仅依赖于ContentProvider,如果按照最开始的我们提供那种架构的话,UI会依赖于获取数据的REST-Method,需要等待数据返回后再手动刷新界面。
ContentProvider is a simple way in Android to store and retrieve data across process boundaries. Typically , a ContentProvider sits in front of the database.
Use the ContentProvider and sync adapter
SyncAdapter: what it is the ability of the system to help you synchronize remote and local content. The sync adapters are simply services started by the sync manager(sync manager manage sync-adapter from all apps).
AyncAdapter 是交由系统管理的,可以避免同一时刻不同App同时进行网络操作,数据库操作这些,使用AyncAdapter有利于整体优化系统性能,Google的Email、Gmail自带app都有使用。
Conclusions
- Do not implememt REST methods inside Activities
- Start long running opertions from a Service
- Persist early & persist often
- Minimize the nerwork usage
- Use a sync adapter to execute background operations which ara not time critical
基于数据库的数据需要及时的清理旧的数据,因为数据库的游标最多可以持有1M的数据,如果超出1M,他就会做Windowing(怎么译?)这个操作非常之慢~~~
nTop 30 March 2015